Comparison Heatspreader - Heat Sink (LAN-070e.A2) Guide
Table of Contents
Introduction
The operation of electronic components generates power loss in the form of heat. The component must dissipate this heat to its environment in some way. Otherwise, it will overheat and could be permanently damaged. Normally, this heat flow occurs by convection through the component's housing to the surrounding air. However, if a component generates a lot of heat, this path is no longer sufficient and heat dissipation must be improved with the aid of additional components.
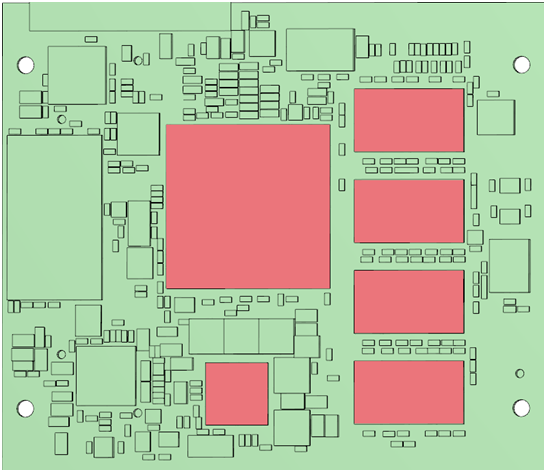
The PHYTEC modules can have several components/zones (hot spots) where heat must be especially dissipated.
Note
This manual can be used for all PHYTEC products. The examples shown here are from the phyFLEX-i.MX 6.
The following chapter briefly explains the two tools for improving heat dissipation, heat sinks and heat spreaders.
Aids to Improve Heat Dissipation
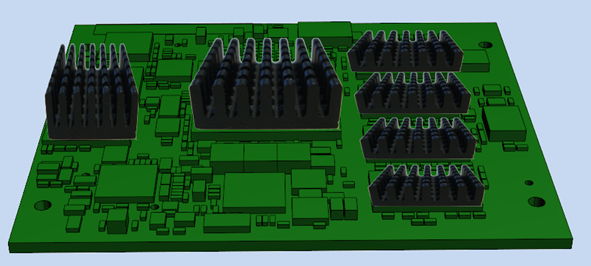
Heat Sink
A heat sink is a component for improving heat dissipation and, as a result, lowers the temperature of a heat source. A measure of the heat dissipation capacity of a heat sink is the thermal resistance RTH.
In this context, the heat sink is at the end of the heat flow and dissipates the heat to the ambient air. If it is used in a closed housing, the surrounding air will of course heat up in the long run. This reduction in the difference between the heat source and the heat sink means that the component in question can be cooled less and less effective.
Heatspreader
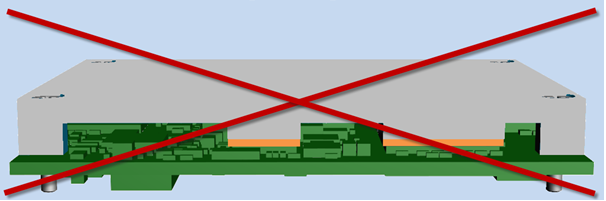
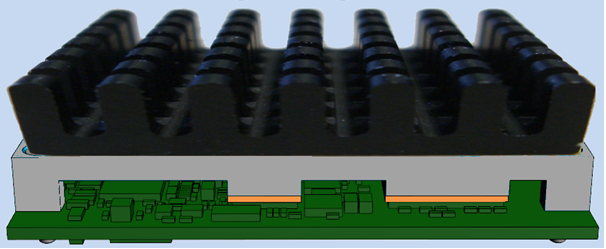
The task of the heatspreader is to distribute/convey the heat loss. Due to its shape, which is specifically adapted to the respective circuit board, the heat spreader picks up several heat sources at the same time and brings the waste heat together on a flat surface. From here, it can easily be fed to a heat sink or another heat dissipator (e.g. housing).
Warning
The heatspreader itself is not a heat sink/cooling element, but only a heat conductor. In other words, a heatspreader must always be used together with a heat sink!
Revision History
| Version | Changes to the Manual | Release Date |
| LAN-070d_1 | First Edition | 16.08.2016 |
| LAN-070e.A2 | English Translation | 20.07.2021 |